To set up a router, you don’t necessarily need to call a specialist to your home. You can do it yourself. A detailed guide will help you configure the router.
Steps to Configure Your Router
First, you need to choose a convenient location to install the router. The steps to configure the router are as follows:
- Connect the router’s power source, then turn it on by pressing the power button.
- Connect the internet modem to the router. The port for the cable might be labeled WAN, uplink, or Internet.

- Use a network cable to connect the router to your computer. Next to the port for this connection, you’ll see numbered ports. Plug one end of the cable into one of these numbered ports and the other end into the internet port on your PC (it usually has an icon of three computers nearby).
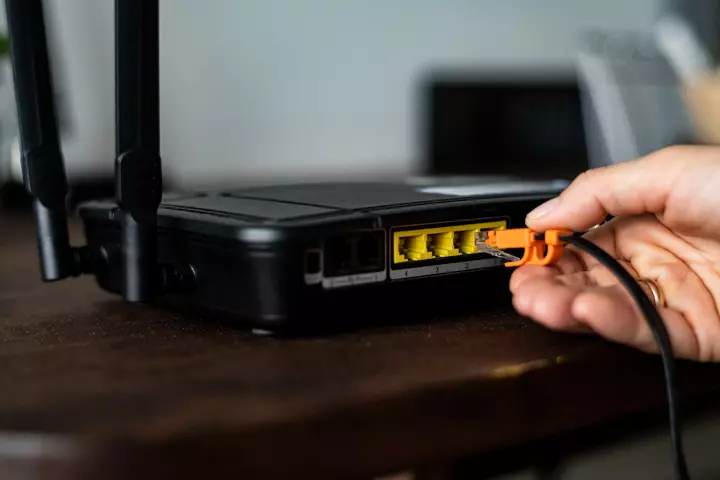

How to Access the Router’s Settings?
Open the router’s administration console. On the computer connected to the router, launch a web browser. Then, type the router’s network administration address into the address bar and press Enter to access the device’s homepage. Many routers are accessible via the web address http://192.168.1.1 or http://192.168.0.1. If neither address works, check the router’s casing or manual for the correct one.
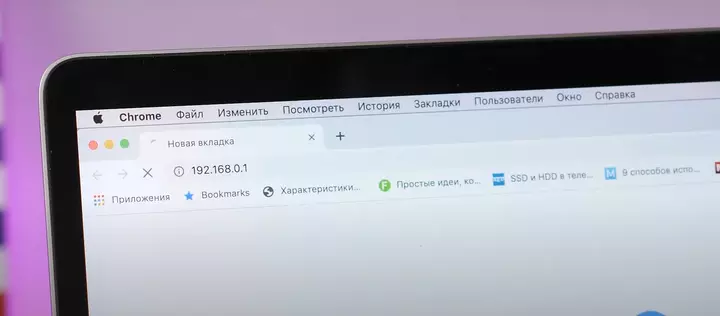
Log into the router. On the router’s homepage, you’ll be prompted to enter a username and password. Both are typically listed in the router’s documentation.
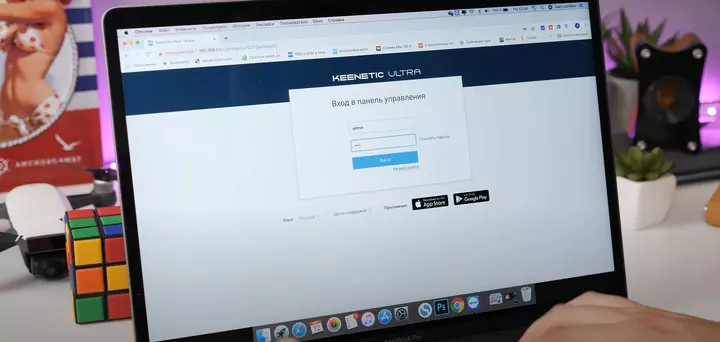
How to Connect the Router to Your Internet Provider?
- Most internet providers automatically send settings to the router once the internet cable is connected. To verify this, open a new browser tab and try visiting a few websites. If they load, the setup is complete, and you can skip this step.
- If there’s still no internet connection, you’ll need to configure the device manually. To do this, go to the WAN, “Internet,” or similarly named section (depending on your router model) and enter the required settings in the appropriate fields. Typically, this includes a login, password, and network protocol (e.g., PPPoE or L2TP) as required by your provider. These details should be in your internet service contract or available in your provider’s online account portal.
- Next, go to the “Wi-Fi Network,” “Wireless Network,” or similar section. Select the WPA2-PSK encryption standard. In the password field, enter a combination to secure your Wi-Fi.
- In the same section, choose the Wi-Fi standard 802.11ac if available, and select the Wi-Fi band (2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, or both). These settings can improve Wi-Fi speed.
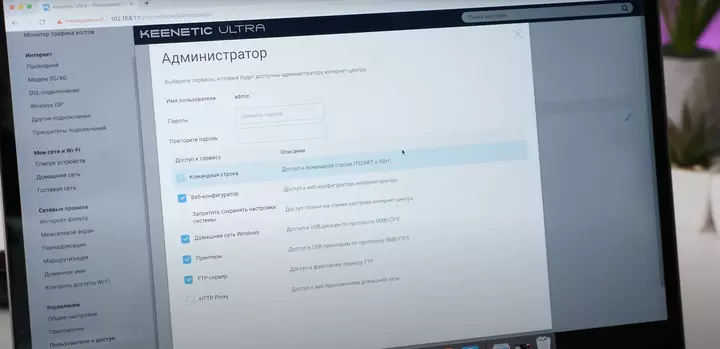
- Protect the router with a password in the “System,” “Device,” “System Tools,” or similar section. Change the default password to a custom one to prevent unauthorized access to the router’s settings.
- Place the router in an optimal location for use.
- The steps above apply to most router models and providers. If you can’t configure the router using these instructions, contact your provider’s support team. A specialist will guide you through the process step by step.
Possible Issues and Nuances When Setting Up a Router
When connecting devices with network cables, ensure each end is securely plugged in. Loose cables are one of the most common causes of network setup issues. After connecting the cable, power cycle the modem (turn it off and back on) so the router can recognize it.
If you bought a used router or previously used it with another provider, reset it to factory settings first. There’s usually a Reset button on the router’s casing—press and hold it for a few seconds to perform the reset. Then proceed with the setup.
Sometimes, identifying the router’s address can be tricky. You can find the device’s IP address using the command line:
- In the Windows search bar, type cmd.
- Open Command Prompt from the list.
- Type ipconfig and press Enter.
- The router’s IP address will appear next to “Default Gateway.”

If this address differs from the standard one (mentioned earlier or in the documentation), the router may have been configured for a specific network with unique requirements. Reset it to factory settings. If no address appears, try resetting the router as well. If that doesn’t help, disconnect the provider’s cable from the router, leaving only the cable connected to the computer. This might resolve the issue: configure the settings without the provider’s cable, then reconnect it once everything is set up.
Also, check the firmware version and update it if needed. If none of this works, ensure your computer’s network card has the correct drivers installed—ideally downloaded from the manufacturer’s official website.
If the settings don’t save after clicking “Save,” or if you can’t restore previous settings from a saved file, try using a different browser. This can help with any unusual behavior in the router’s admin panel.
The best spot for your router is an open, central area of your home. This ensures the most even Wi-Fi coverage. Avoid restricting its range and consider physical obstacles—fewer walls, furniture, or objects between the router and your devices will improve wireless performance.
Every PC user can set up and configure a router themselves. If you encounter any issues with setup or use, reach out to a specialist through your provider’s support team.